Page 189 - Rollingbearings
P. 189
Cages
Cages
For small electric motors, values of between Cages are mechanically stressed during
0,005 and 0,01 are used for the factor k. If bearing operation by frictional, impact, cen-
preload is used primarily to protect the bear- trifugal and inertial forces. They can also be
ing from the damage caused by external The main cage types are described in Com- chemically inluenced by certain organic solv-
vibrations when stationary, then greater ponents and materials, page 24. Additionally, ents or coolants, lubricants, and lubricant
preload is required and k = 0,02 should be information about standard cages, and pos- additives. Therefore, the material type used
used. sible cage options, for a particular bearing for a cage has a signiicant inluence on the
Spring loading is also a common method type is given in the relevant product section. suitability of a rolling bearing for a particular
of applying preload to angular contact ball If a bearing with a non -standard cage is application.
bearings in high-speed grinding spindles. required, check availability before ordering.
The method is not suitable for bearing appli- There are fundamental design differences
cations where a high degree of stiffness is between bearings which, together with the
required, where the direction of axial load inluence of bearing size, make certain cage
changes, or where undeined peak loads can designs necessary. For example:
occur.
For additional information, refer to • some bearing types need either split or
Bearing preload, (skf.com/go/17000-B7). snap-type cages, because they are
assembled after the rings and rolling ele-
ments have been sub-assembled
• other bearing types need roller-guided
Bearing tolerance • bearings of a certain combination of size
cages, to be self-containing
class and series need ring-guided cages, to limit
contact stress between rolling elements
and cage
The dimensional and geometrical tolerances
of bearings are described by their tolerance Given the speciic functional demands and
classes (Tolerances, page 36). In addition to quantity of bearings being manufactured,
the Normal, P6 and P5 tolerance classes, the material and manufacturing methods
SKF also manufactures bearings with even are chosen to provide the most reliable and
narrower tolerances. These include P4, UP cost-effective cage.
and other tolerance classes. For information
about SKF bearings that have a tolerance Bearing execution
class better than P5, refer to
skf.com/super-precision.
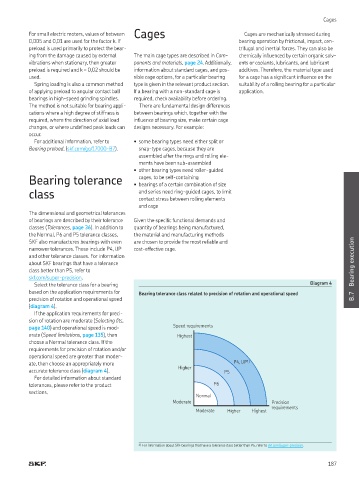
Select the tolerance class for a bearing Diagram 4
based on the application requirements for Bearing tolerance class related to precision of rotation and operational speed
precision of rotation and operational speed B.7
(diagram 4).
If the application requirements for preci-
sion of rotation are moderate (Selecting its,
page 140) and operational speed is mod- Speed requirements
erate (Speed limitations, page 135), then Highest
choose a Normal tolerance class. If the
requirements for precision of rotation and/or
operational speed are greater than moder-
ate, then choose an appropriately more P4, UP 1)
Higher
accurate tolerance class (diagram 4). P5
For detailed information about standard
tolerances, please refer to the product P6
sections.
Normal
Moderate Precision
requirements
Moderate Higher Highest
1) For information about SKF bearings that have a tolerance class better than P5, refer to skf.com/super-precision.
187