Page 187 - Rollingbearings
P. 187
Selecting internal clearance or preload
Start-up Required minimum initial • Bearing types for adjusted bearing
During start-up, the temperature gradient internal clearance arrangements – such as angular contact
over the bearing is largely determined by the ball bearings, tapered roller bearings or
transient heat low Among the various com- The required minimum initial internal clear- spherical roller thrust bearings – have
ponents in contact with the bearing, the one ance can be estimated using their internal clearance set during mount-
that has the smallest thermal capacity will ing (Mounting adjusted bearing arrange-
rise in temperature faster than the one that r = r + Δr + Δr temp + Δr other ments, page 203)
it
op
has the largest thermal capacity Therefore, • For other bearing types, select a bearing
the start-up sequence can result in a larger where clearance class (Internal clearance,
temperature differential between bearing r = required minimum initial internal page 26: Normal, C3, C4, etc ) whose
inner and outer ring than in the steady-state clearance [μm] minimum clearance is equal to or greater
condition It results in a temperature peak r = required operating clearance [μm] than the estimated minimum initial inter-
op
during start-up (ΔT max in diagram 3) This is Δr = clearance change caused by the nal clearance (ig.3) Then verify whether
it
especially pronounced in machines that maximum expected its [μm] the resulting maximum clearance of the
either are working outdoors in a cold climate Δr temp = maximum clearance change selected clearance class is acceptable for
or have a heated shaft expected from the temperature the application If the maximum clearance,
difference during start-up or in for whatever reason, is too large then con-
Higher speeds steady state [μm] sider choosing a reduced clearance group
Δr other = maximum clearance change – e g C3L, which includes only the lower
Whether during start-up or at steady state, expected from other effects such as half of the C3 clearance group range
higher speeds generate larger frictional axial clamping [μm]
losses This typically results in a larger tem-
perature differential between the bearing
inner and outer ring and therefore a need for
larger initial clearance
Other inluences on
clearance/preload
Axial clamping of a ring results in a small
increase of its diameter Normally, this has a
negligible inluence For machines where Bearing execution
there is a large axial load on any of the rings,
or where two bearings (e g angular contact
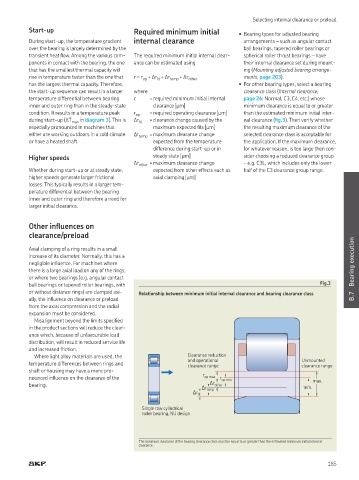
ball bearings or tapered roller bearings, with Fig.3
or without distance rings) are clamped axi- Relationship between minimum initial internal clearance and bearing clearance class
ally, the inluence on clearance or preload B.7
from the axial compression and the radial
expansion must be considered
Misalignment beyond the limits speciied
in the product sections will reduce the clear-
ance which, because of unfavourable load
distribution, will result in reduced service life
and increased friction
Where light alloy materials are used, the Clearance reduction
temperature differences between rings and and operational Unmounted
clearance range clearance range
shaft or housing may have a more pro-
r op max
nounced inluence on the clearance of the r op min
max
bearing Δr other
Δr temp min
Δr it
Single row cylindrical
roller bearing, NU design
The minimum clearance of the bearing clearance class must be equal to or greater than the estimated minimum initial internal
clearance
185