Page 186 - Rollingbearings
P. 186
B.7 Bearing execution
Range of initial internal Clearance reduction caused Clearance reduction caused
clearance by interference its by temperature difference
between shaft, bearing rings
Bearing types for adjusted bearing arrange- An interference it causes clearance reduc- and housing
ments – such as angular contact ball bear- tion because inner rings are expanded and
ings, tapered roller bearings and spherical outer rings are compressed. The reduction The temperature behaviour of an application
roller thrust bearings – have their internal equals the effective interference it multi- can create a difference in temperature
clearance set during mounting The internal plied by a reduction factor using between a bearing inner ring and outer ring,
clearance of such an arrangement, even which changes the mounted bearing clear-
though set by adjustment during mounting, Δr = Δ f + Δ f ance/preload. For a steel shaft and steel or
2 2
1 1
it
will nevertheless have a range cast iron housing, the change can be esti-
For other bearing types, the initial internal where mated using
clearance is determined during their manu- Δr = clearance reduction caused by the it
it
facture. ISO has deined ive clearance [μm] Δr temp = 0,012 ΔT d m
classes for specifying the degree of initial f = reduction factor for the inner ring
1
internal clearance in a bearing (Internal f = reduction factor for the outer ring where
2
clearance, page 26). Each clearance class Δ = effective interference between the Δr temp = clearance reduction caused by
1
represents a range of values. The size of the inner ring and shaft [μm] temperature difference [μm]
ranges varies depending on bearing type Δ = effective interference between the ΔT = temperature difference between
2
and size. Clearance class details are listed in outer ring and housing [μm] inner and outer ring [°C]
relevant product sections. d = the bearing mean diameter [mm]
m
Initial clearances greater than Normal, Reduction factors valid for a solid steel shaft = (d + D)/2
such as C3 or even C4 clearance classes, are and a thick-walled cast iron or steel housing
very common today. This is because modern can be obtained from diagram 2 as a func- Steady state
bearings take higher loads and require tion of the ratio of the bearing bore diameter
tighter interference its, and typical operat- d to the outside diameter D. For the effective The operating temperature of a bearing
ing conditions are different, compared to interference value, use the maximum prob- reaches a steady state when there is thermal
when the clearance classes were deined. able interference value listed in the appro- equilibrium (page 131) – i.e. there is a bal-
For universally matchable single row priate tables in Tolerances and resultant its, ance between generated heat and dissipated
Bearing execution tapered roller bearings, double row angular using SKF calculation tools, such as SKF ent temperature of the surroundings of the
heat. In the common case where the ambi-
angular contact ball bearings and matched
page 153.
For a more detailed analysis, consider
contact ball bearings and four-point contact
housing of a bearing arrangement is cooler
than its shaft, a steady-state temperature
ball bearings, values for the axial internal
Bearing Calculator (skf.com/bearingcalculator),
gradient is developed that results in the
SKF SimPro Quick or SKF SimPro Expert, or
clearance are given instead of radial internal
contact the SKF application engineering
inner ring of the bearing being hotter than
clearance, because the axial clearance is of
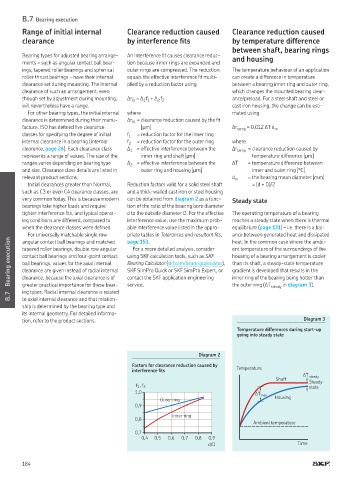
B.7 greater practical importance for these bear- service. the outer ring (ΔT steady in diagram 3).
ing types. Radial internal clearance is related
to axial internal clearance and that relation-
ship is determined by the bearing type and
its internal geometry. For detailed informa-
tion, refer to the product sections. Diagram 3
Temperature differences during start-up
going into steady state
Diagram 2
Factors for clearance reduction caused by
interference its Temperature
ΔT steady
Shaft
Steady
f 1 , f 2 state
1,0
ΔT max
Outer ring Housing
0,9
Inner ring
0,8
Ambient temperature
0,7
0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9
d/D Time
184