Page 133 - Rollingbearings
P. 133
Thermal equilibrium
Bearing size, Thermal Generated heat
operating equilibrium The heat generated is the sum of:
temperature and • heat generated by the bearing, as a result
lubrication conditions The operating temperature of a bearing of the combined bearing and seal frictional
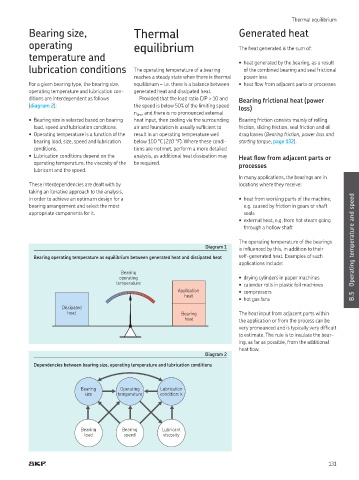
reaches a steady state when there is thermal power loss
For a given bearing type, the bearing size, equilibrium – i.e. there is a balance between • heat low from adjacent parts or processes
operating temperature and lubrication con- generated heat and dissipated heat.
ditions are interdependent as follows Provided that the load ratio C/P > 10 and Bearing frictional heat (power
(diagram 2): the speed is below 50% of the limiting speed loss)
n , and there is no pronounced external
lim
• Bearing size is selected based on bearing heat input, then cooling via the surrounding Bearing friction consists mainly of rolling
load, speed and lubrication conditions. air and foundation is usually suficient to friction, sliding friction, seal friction and oil
• Operating temperature is a function of the result in an operating temperature well drag losses (Bearing friction, power loss and
bearing load, size, speed and lubrication below 100 °C (210 °F) Where these condi- starting torque, page 132)
conditions. tions are not met, perform a more detailed
• Lubrication conditions depend on the analysis, as additional heat dissipation may Heat low from adjacent parts or
operating temperature, the viscosity of the be required processes
lubricant and the speed.
In many applications, the bearings are in
These interdependencies are dealt with by locations where they receive:
taking an iterative approach to the analysis,
in order to achieve an optimum design for a • heat from working parts of the machine,
bearing arrangement and select the most e g caused by friction in gears or shaft
appropriate components for it. seals
• external heat, e g from hot steam going
through a hollow shaft
The operating temperature of the bearings Operating temperature and speed
Diagram 1 is inluenced by this, in addition to their
Bearing operating temperature as equilibrium between generated heat and dissipated heat self-generated heat Examples of such
applications include:
Bearing
operating • drying cylinders in paper machines
temperature • calender rolls in plastic foil machines
Application • compressors
heat B.5
• hot gas fans
Dissipated
heat Bearing The heat input from adjacent parts within
heat the application or from the process can be
very pronounced and is typically very dificult
to estimate The rule is to insulate the bear-
ing, as far as possible, from the additional
heat low
Diagram 2
Dependencies between bearing size, operating temperature and lubrication conditions
Bearing Operating Lubrication
size temperature condition: k
Bearing Bearing Lubricant
load speed viscosity
131