Page 136 - Rollingbearings
P. 136
B.5 Operating temperature and speed
Cooling via Diagram 5
circulating oil Relationship between power loss, heat dissipation and temperature
By circulating the oil, it is possible to cool it,
and thereby remove heat from the bearing Power
arrangement
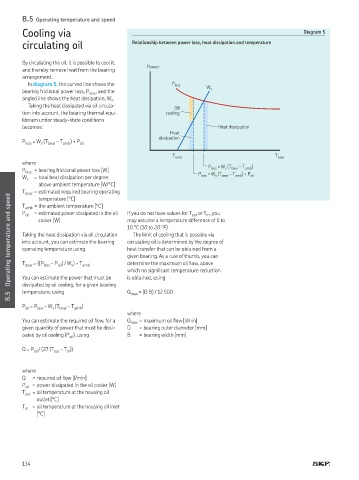
In diagram 5, the curved line shows the P loss W
bearing frictional power loss, P loss , and the s
angled line shows the heat dissipation, W
s
Taking the heat dissipated via oil circula- Oil
tion into account, the bearing thermal equi- cooling
librium under steady-state conditions
becomes: Heat dissipation
Heat
dissipation
P loss = W (T bear – T amb ) + P
oil
s
T amb T bear
where P = W (T – T )
P loss = bearing frictional power loss [W] P loss s bear amb
W = total heat dissipation per degree loss = W s (T bear – T amb ) + P oil
s
above ambient temperature [W/°C]
T bear = estimated required bearing operating If you do not have values for T out or T , you
Operating temperature and speed Taking the heat dissipation via oil circulation may assume a temperature difference of 5 to
temperature [°C]
T
= the ambient temperature [°C]
amb
P = estimated power dissipated in the oil
oil
in
cooler [W]
10 °C (10 to 20 °F)
The limit of cooling that is possible via
into account, you can estimate the bearing
circulating oil is determined by the degree of
operating temperature using
heat transfer that can be obtained from a
given bearing As a rule of thumb, you can
T
= ((P
determine the maximum oil low, above
– P ) / W ) + T
amb
oil
loss
s
bear
is obtained, using
dissipated by oil cooling, for a given bearing
Q
temperature, using
= (D B) / 12 500
B.5 You can estimate the power that must be which no signiicant temperature reduction
max
P = P loss - W (T bear – T amb )
s
oil
where
You can estimate the required oil low, for a Q max = maximum oil low [l/min]
given quantity of power that must be dissi- D = bearing outer diameter [mm]
pated by oil cooling (P ), using B = bearing width [mm]
oil
Q = P / (27 (T out – T ))
in
oil
where
Q = required oil low [l/min]
P = power dissipated in the oil cooler [W]
oil
T out = oil temperature at the housing oil
outlet [°C]
T = oil temperature at the housing oil inlet
in
[°C]
134