Page 135 - Rollingbearings
P. 135
Estimating bearing operating temperature
Starting torque Estimating heat
dissipation from SKF
The starting torque of a rolling bearing is
deined as the frictional moment that must plummer (pillow)
be overcome by the bearing to start rotating,
at an ambient temperature of 20 to 30 °C blocks
(70 to 85 °F) Therefore, only the sliding fric-
tional moment and the frictional moment of For SKF plummer (pillow) block housings,
seals, if applied, are taken into consideration you can use a model based on bearing size
to estimate heat dissipation values
M start = M + M seal Using diagram 4, you can estimate the
sl
heat dissipation per degree above ambient
temperature, W , for a bearing with bearing
s
where mean diameter d in a plummer block hous-
m
M start = starting frictional moment [Nmm] ing, with the shaft exposed to the surround-
M = sliding frictional moment [Nmm] ing air
sl
M seal = frictional moment of the seals [Nmm] The estimation is valid for SKF plummer
block housings used with grease or oil bath
We recommend using the SKF Bearing lubrication and only where there is no signif-
Calculator (skf com/bearingcalculator) for icant heat input from external sources, such
calculating starting torque values as steam heating of shafts or pronounced
radiation from hot surfaces
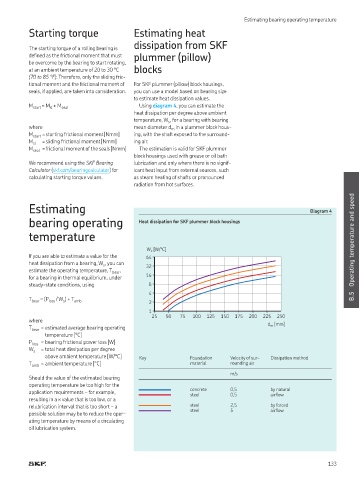
Estimating Diagram 4
bearing operating Heat dissipation for SKF plummer block housings
temperature Operating temperature and speed
W s [W/°C]
If you are able to estimate a value for the 64
heat dissipation from a bearing, W , you can 32
s
estimate the operating temperature, T bear ,
for a bearing in thermal equilibrium, under 16
steady-state conditions, using 8
4 B.5
T bear = (P loss / W ) + T amb 2
s
1
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
where
d m [mm]
T bear = estimated average bearing operating
temperature [°C]
P loss = bearing frictional power loss [W]
W = total heat dissipation per degree
s
above ambient temperature [W/°C] Key Foundation Velocity of sur- Dissipation method
T amb = ambient temperature [°C] material rounding air
m/s
Should the value of the estimated bearing
operating temperature be too high for the
application requirements – for example, concrete 0,5 by natural
steel
0,5
airlow
resulting in a κ value that is too low, or a
relubrication interval that is too short – a steel 2,5 by forced
steel 5 airlow
possible solution may be to reduce the oper-
ating temperature by means of a circulating
oil lubrication system
133