Page 30 - Rollingbearings
P. 30
A.1 Bearing basics
Standardized For thrust bearings, height series are used Bearings with inch
instead of width series. Height series are
boundary numbered 7, 9, 1 and 2. dimensions
Bearings to ISO general plans have the
dimensions same boundary dimensions when they share In addition to the bearings in accordance
the same bore diameter and dimension with ISO dimensions, SKF has a comprehen-
series (table 3). If not, they have different sive assortment of bearings with inch
Boundary dimensions are the main dimen- boundary dimensions. dimensions following American and British
sions of a bearing (ig. 25 and ig. 26). They standards.
comprise:
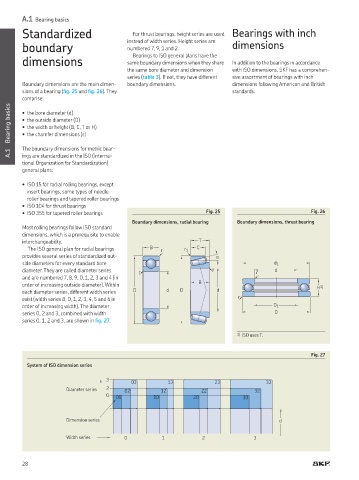
Bearing basics • the bore diameter (d)
• the outside diameter (D)
• the width or height (B, C, T or H)
• the chamfer dimensions (r)
A.1 The boundary dimensions for metric bear-
ings are standardized in the ISO (Interna-
tional Organization for Standardization)
general plans:
• ISO 15 for radial rolling bearings, except
insert bearings, some types of needle
roller bearings and tapered roller bearings
• ISO 104 for thrust bearings
• ISO 355 for tapered roller bearings Fig. 25 Fig. 26
Boundary dimensions, radial bearing Boundary dimensions, thrust bearing
Most rolling bearings follow ISO standard
dimensions, which is a prerequisite to enable
interchangeability. T
The ISO general plan for radial bearings B r r 1 C
provides several series of standardized out- α
side diameters for every standard bore d 1
diameter. They are called diameter series r r r d
and are numbered 7, 8, 9, 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4 (in
order of increasing outside diameter). Within B H
1)
each diameter series, different width series D d D d
exist (width series 8, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 in r
order of increasing width). The diameter D 1
series 0, 2 and 3, combined with width D
series 0, 1, 2 and 3, are shown in ig. 27.
1) ISO uses T.
Fig. 27
System of ISO dimension series
3
03 13 23 33
Diameter series 2 02 12 22 32
0 00 10 20 30
Dimension series d
Width series 0 1 2 3
28