Page 29 - Rollingbearings
P. 29
Heat and surface treatment
Heat and surface Hardening Dimensional stability
treatment There are three typical hardening methods Heat treatment is used to limit dimensional
that may be applied to bearing components: changes caused by metallurgical effects at
extreme temperatures. There is a standard-
Rolling bearing rings and rolling elements • Through-hardening ized classiication system for dimensional
must: This is the standard method for most stability (table 2). The various SKF bearing
bearings and provides good fatigue and types are stabilized to different classes as
• be hard enough to cope with fatigue and wear-resistance, as hardening is applied standard.
plastic deformations over the full cross section.
• be tough enough to cope with applied
loads • Induction-hardening
• be suficiently stable to experience only Surface induction-hardening is used to Surface treatment Bearing basics
limited changes of dimensions over time selectively harden a component’s raceway and coatings
to limit rolling contact fatigue, leaving the
The required properties are achieved by heat remainder of the component unaffected to
and surface treatments. maintain structural strength. Coating is a well-established method for
providing bearings with additional functional A.1
• Case-hardening beneits to accommodate speciic application
Case-hardening provides hardness to the conditions. Widely used coatings are zinc
surface. It is used, for example, where chromate and black oxide.
bearing rings are subjected to high shock Two other methods developed by SKF
loads causing structural deformations. have proven successful in many applications:
• INSOCOAT bearings are standard bearings
that have the external surfaces of their
inner or outer ring coated with an alumin-
ium oxide layer. This coating increases
resistance to electric current through the
bearing.
• NoWear enhances wear-resistance of the
raceway or rolling element surfaces. It can
help the bearing withstand long periods of
operation under poor lubrication conditions
and to reduce the risk for low load damage.
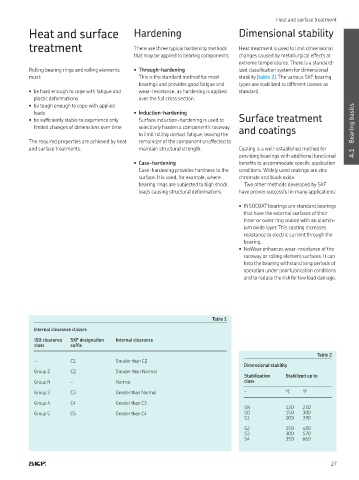
Table 1
Internal clearance classes
ISO clearance SKF designation Internal clearance
class sufix
Table 2
– C1 Smaller than C2
Dimensional stability
Group 2 C2 Smaller than Normal
Stabilization Stabilized up to
Group N – Normal class
Group 3 C3 Greater than Normal – °C °F
Group 4 C4 Greater than C3
SN 120 250
Group 5 C5 Greater than C4 S0 150 300
S1 200 390
S2 250 480
S3 300 570
S4 350 660
27