Page 224 - Rollingbearings
P. 224
Rope sheave
C.2 Rope sheave
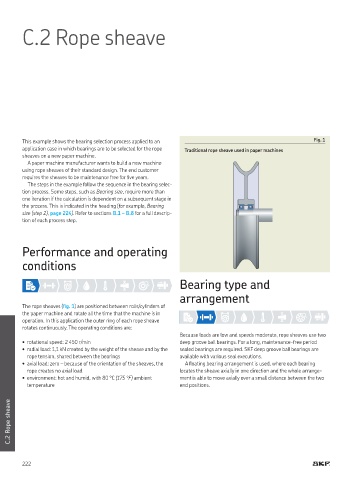
This example shows the bearing selection process applied to an Fig. 1
application case in which bearings are to be selected for the rope Traditional rope sheave used in paper machines
sheaves on a new paper machine
A paper machine manufacturer wants to build a new machine
using rope sheaves of their standard design The end customer
requires the sheaves to be maintenance free for ive years.
The steps in the example follow the sequence in the bearing selec-
tion process. Some steps, such as Bearing size, require more than
one iteration if the calculation is dependent on a subsequent stage in
the process. This is indicated in the heading (for example, Bearing
size (step 2), page 224). Refer to sections B.1 – B.8 for a full descrip-
tion of each process step.
Performance and operating
conditions
Bearing type and
arrangement
The rope sheaves (ig. 1) are positioned between rolls/cylinders of
the paper machine and rotate all the time that the machine is in
operation. In this application the outer ring of each rope sheave
rotates continuously. The operating conditions are:
Because loads are low and speeds moderate, rope sheaves use two
• rotational speed: 2 450 r/min deep groove ball bearings. For a long, maintenance-free period
• radial load: 1,1 kN created by the weight of the sheave and by the sealed bearings are required. SKF deep groove ball bearings are
rope tension, shared between the bearings available with various seal executions.
• axial load: zero – because of the orientation of the sheaves, the A loating bearing arrangement is used, where each bearing
rope creates no axial load locates the sheave axially in one direction and the whole arrange-
• environment: hot and humid, with 80 °C (175 °F) ambient ment is able to move axially over a small distance between the two
temperature end positions.
C.2 Rope sheave
222