Page 209 - Rollingbearings
P. 209
Mounting and dismounting
During the test run, or immediately after- Dismounting bearings itted
wards, check the seals, any lubrication sys- on a cylindrical shaft seat
tems and all luid levels If noise and vibra-
tion levels are severe, it is advisable to check Cold dismounting
the lubricant for signs of contamination
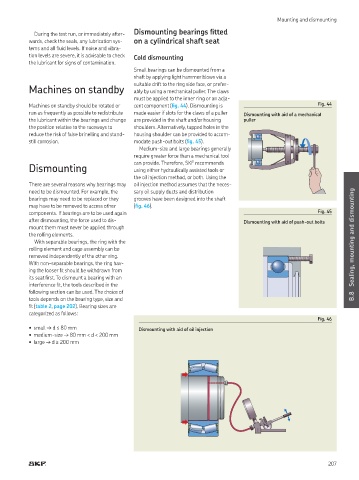
Small bearings can be dismounted from a
shaft by applying light hammer blows via a
suitable drift to the ring side face, or prefer-
Machines on standby ably by using a mechanical puller The claws
must be applied to the inner ring or an adja-
Machines on standby should be rotated or cent component (ig. 44) Dismounting is Fig. 44
run as frequently as possible to redistribute made easier if slots for the claws of a puller Dismounting with aid of a mechanical
the lubricant within the bearings and change are provided in the shaft and/or housing puller
the position relative to the raceways to shoulders Alternatively, tapped holes in the
reduce the risk of false brinelling and stand- housing shoulder can be provided to accom-
still corrosion modate push-out bolts (ig. 45)
Medium-size and large bearings generally
require greater force than a mechanical tool
can provide Therefore, SKF recommends
Dismounting using either hydraulically assisted tools or
the oil injection method, or both Using the
There are several reasons why bearings may oil injection method assumes that the neces-
need to be dismounted For example, the sary oil supply ducts and distribution
bearings may need to be replaced or they grooves have been designed into the shaft
may have to be removed to access other (ig. 46)
components If bearings are to be used again Fig. 45
after dismounting, the force used to dis- Dismounting with aid of push-out bolts
mount them must never be applied through
the rolling elements Sealing, mounting and dismounting
With separable bearings, the ring with the
rolling element and cage assembly can be
removed independently of the other ring
With non-separable bearings, the ring hav-
ing the looser it should be withdrawn from
its seat irst To dismount a bearing with an
interference it, the tools described in the
following section can be used The choice of
tools depends on the bearing type, size and B.8
it (table 2, page 202) Bearing sizes are
categorized as follows:
Fig. 46
• small → d ≤ 80 mm Dismounting with aid of oil injection
• medium-size → 80 mm < d < 200 mm
• large → d ≥ 200 mm
207