Page 45 - SKF-bearing-housings
P. 45
1
Design considerations
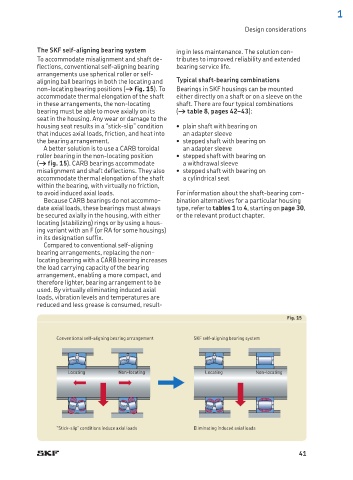
The SKF self-aligning bearing system ing in less maintenance. The solution con-
To accommodate misalignment and shaft de- tributes to improved reliability and extended
flections, conventional self-aligning bearing bearing service life.
arrangements use sp h e r i c a l r o l l e r o r self-
aligning ball bearings in both the locating and Typical shaft-bearing combinations
non-locating bearing positions († fig. 15). To Bearings in SKF housings can be mounted
accommodate thermal elongation of the shaft either directly on a shaft or on a sleeve on the
in these arrangements, the non-locating shaft. There are four typical combinations
bearing must be able to move axially on its († table 8, pages 42–43):
seat in the housing. Any wear or damage to the
housing seat results in a “stick-slip” condition • plain shaft with bearing on
that induces axial loads, friction, and heat into an adapter sleeve
the bearing arrangement. • stepped shaft with bearing on
A better solution is to use a CARB toroidal an adapter sleeve
roller bearing in the non-locating position • stepped shaft with bearing on
(† fig. 15). CARB bearings accommodate a withdrawal sleeve
misalignment and shaft deflections. They also • stepped shaft with bearing on
accommodate thermal elongation of the shaft a cylindrical seat
within the bearing, with virtually no friction,
to avoid induced axial loads. For information about the shaft-bearing com-
Because CARB bearings do not accommo- bination alternatives for a particular housing
date axial loads, these bearings must always type, refer to tables 1 to 4, starting on page 30,
be secured axially in the housing, with either or the relevant product chapter.
locating (stabilizing) rings or by using a hous-
ing variant with an F (or RA for some housings)
in its designation suffix.
Compared to conventional self-aligning
bearing arrangements, replacing the non-
locating bearing with a CARB bearing increases
the load carrying capacity of the bearing
arrangement, enabling a more compact, and
therefore lighter, bearing arrangement to be
used. By virtually eliminating induced axial
loads, vibration levels and temperatures are
reduced and less grease is consumed, result-
Fig. 15
Conventional self-aligning bearing arrangement SKF self-aligning bearing system
Locating Non-locating Locating Non-locating
“Stick-slip” conditions induce axial loads Eliminating induced axial loads
41