Page 89 - Rollingbearings
P. 89
These selection criteria and the related Note that there are applications where both
bearing ratings and static safety factor are selection criteria must be considered, for
shown in diagram 2 and are described in example where a duty cycle has occasional
detail in the relevant subsections peak loads Also, in applications where the
Which selection criteria you should use bearing is lightly loaded, the minimum load
depends on the operating conditions of the requirement (Requisite minimum load,
bearing: page 106) must also be considered
After determining bearing size, and before
• For applications where bearings are run going to the next step, check the items listed
ning in typical operating conditions – i e in Checklist after the bearing size is deter-
normal speeds, good lubrication condi mined, page 106.
tions and not highly or peak loaded – use Other attributes of the bearing compon
Size selection based on rating life, ents, such as strength and suitability, are
page 88 addressed elsewhere in the Bearing selection
• For applications where bearings are run process, including Lubrication, page 110,
ning under very low speeds or which are and Bearing execution, page 182, as well as
used under stationary conditions, very bad in the product sections Consider these
lubrication conditions or where occasional attributes, in addition to bearing size, to
peak loads occur, use Size selection based ensure you obtain best bearing
on static load, page 104 performance
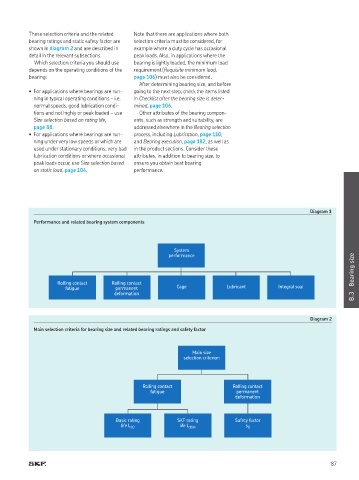
Diagram 1
Performance and related bearing system components
System
Bearing size
performance
Rolling contact Rolling contact
fatigue permanent Cage Lubricant Integral seal
B.3
deformation
Diagram 2
Main selection criteria for bearing size and related bearing ratings and safety factor
Main size
selection criterion
Rolling contact Rolling contact
fatigue permanent
deformation
Basic rating SKF rating Safety factor
life L 10 life L 10m s 0
87